Day 23 : Two-Piece Normal Distribution#
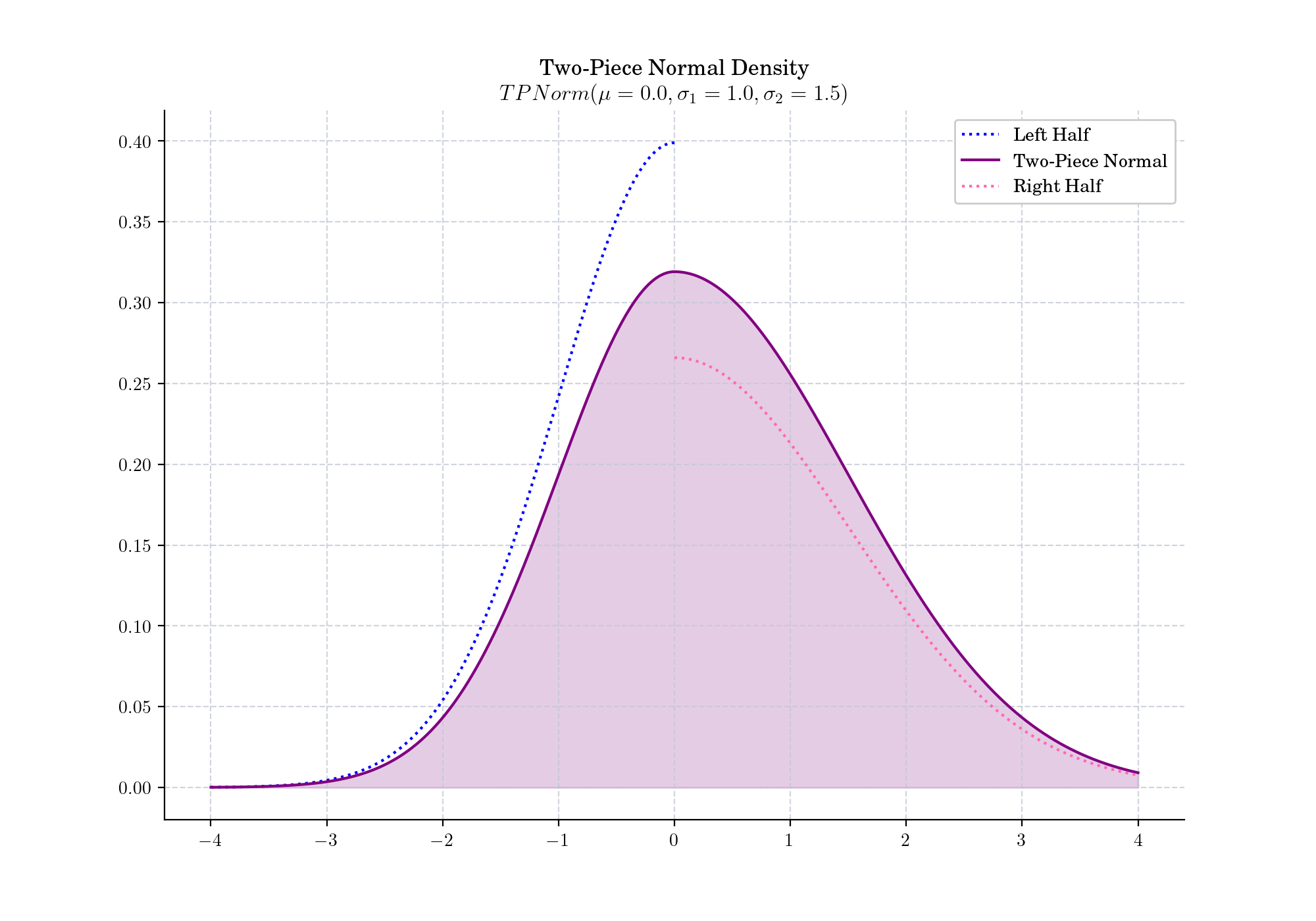
The two-piece normal, also known as split normal, binormal, or double-Gaussian, results from joining at the mode the corresponding halves of two normal distributions with the same mode \(\mu\) but different standard deviations \(\sigma_1\) and \(\sigma_2\). This idea can be seen in the following plot where we can see the two half densities (in blue and pink) and the resulting two-piece normal density (in purple).
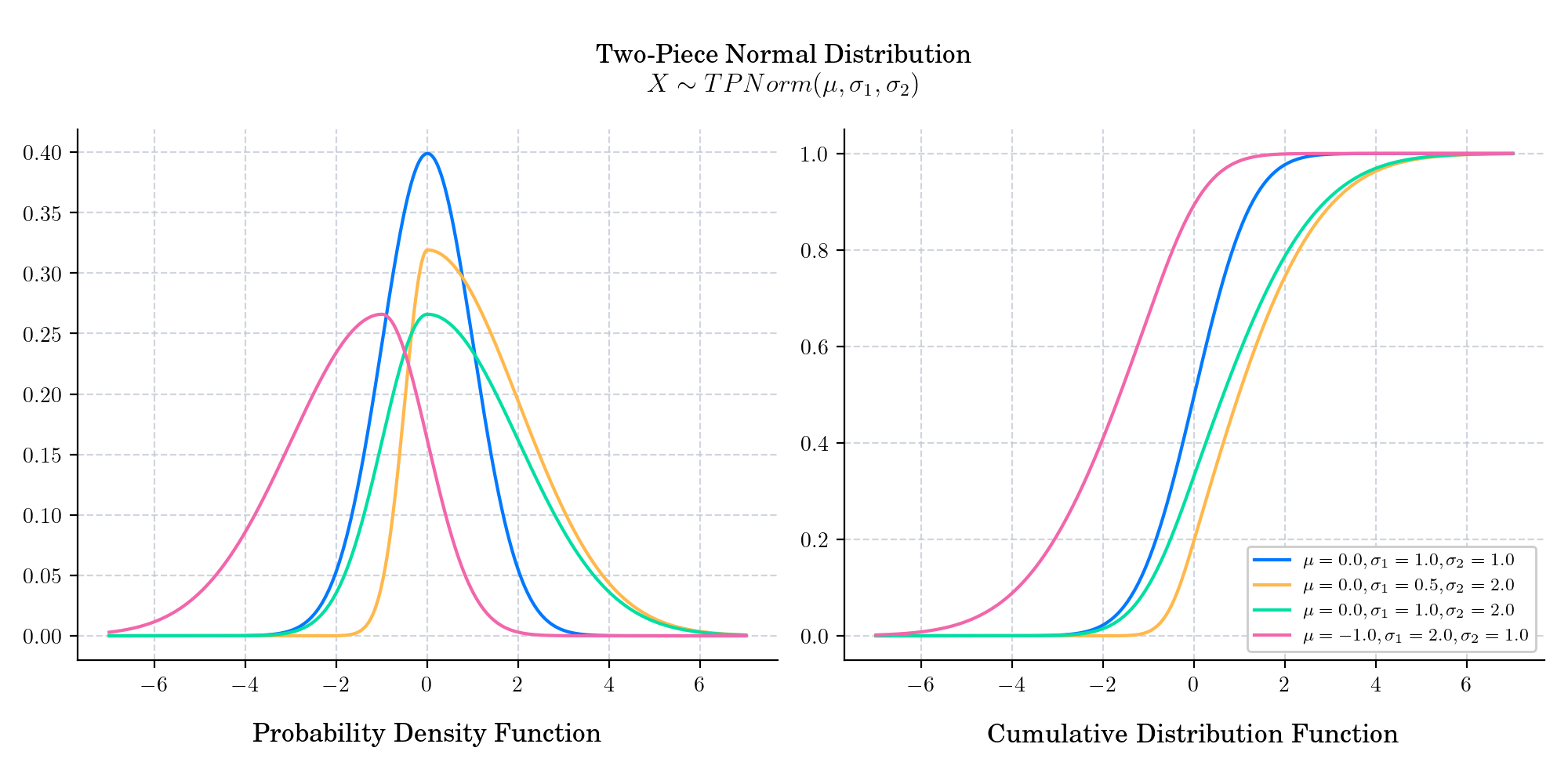
The probability density function is given by
where \(\phi\) denotes the density function of a standard normal distribution.
🔔 Random Facts 🔔#
The two-piece normal was proposed by German physicist and phycologist Gustav Fechner -who is also consider the founder of psychophysics- around 1887 but published posthumously ten years later. Unfortunately, Fechner work did not become popular and this lead to a series of re discoveries (as recent as 2016!).
If \(\sigma_1=\sigma_2\), then the two-piece normal becomes a normal distribution.
The Two-Piece normal, and more generally the family of two-piece distributions, have been extensively used in applications such as:
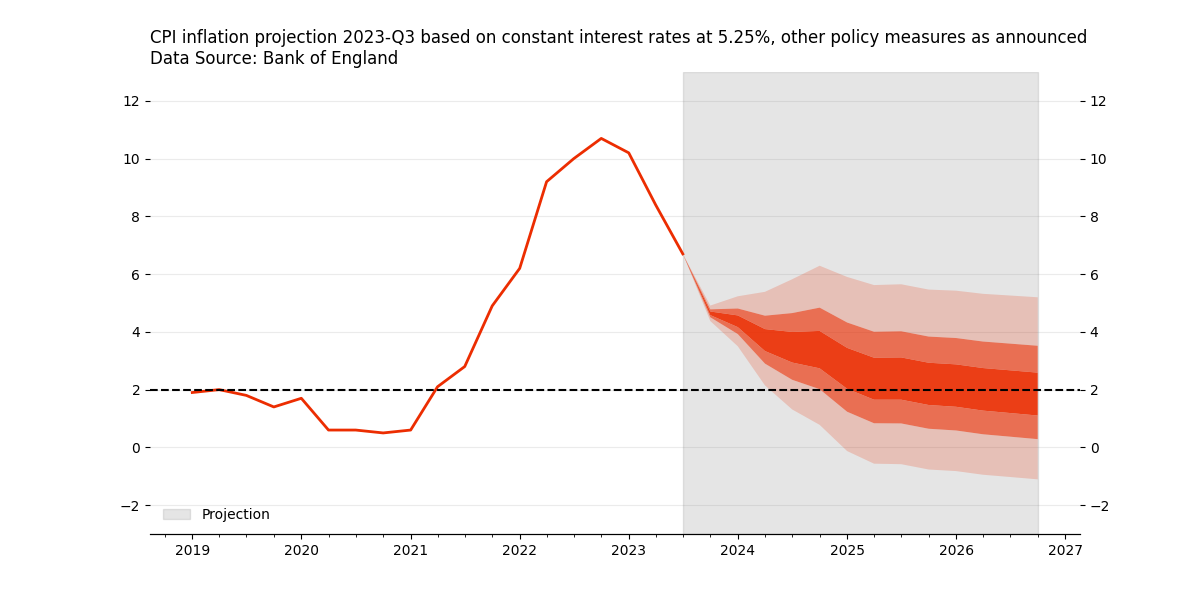
Bank of England Fan Charts for Inflation Report
Measurement Errors Models
Forecasting and Estimation of Risk
Today’s bonus plot is a fan chart showing the historical CPI inflation as well as its projection as of 2023-Q3. The Bank of England uses a two-piece normal distribution to model the quarterly inflation forecasts.