Day 13: Markowitz Efficient Frontier#
“The return on investment is important, but so is the degree of uncertainty surrounding that return.”
—Harry Markowitz, Portfolio Selection: Efficient Diversification of Investments (1959)
The Markowitz Mean–Variance Portfolio Theory (1952) formalizes how rational investors should construct portfolios by balancing expected return against risk (measured as variance or standard deviation).
The Efficient Frontier represents the set of optimal portfolios that: Maximize expected return for a given level of risk, or equivalently minimize risk for a given expected return. Any portfolio below the frontier is inefficient—it delivers less return for the same risk.
To construct the efficient frontier, we consider a set of assets with known expected returns, variances, and covariances. The efficient frontier is derived by solving a series of optimization problems, where we minimize the portfolio variance for different target returns.
Definition. The efficient frontier is defined as the set of portfolios that satisfy the following optimization problem:
where \(w\) is the vector of asset weights in the portfolio, \(\Sigma\) is the covariance matrix of asset returns, \(\mu\) is the vector of expected asset returns, and \(R_t\) is the target return for the portfolio. The efficient frontier can be visualized in a risk-return space, where the x-axis represents the portfolio risk (standard deviation) and the y-axis represents the expected return.
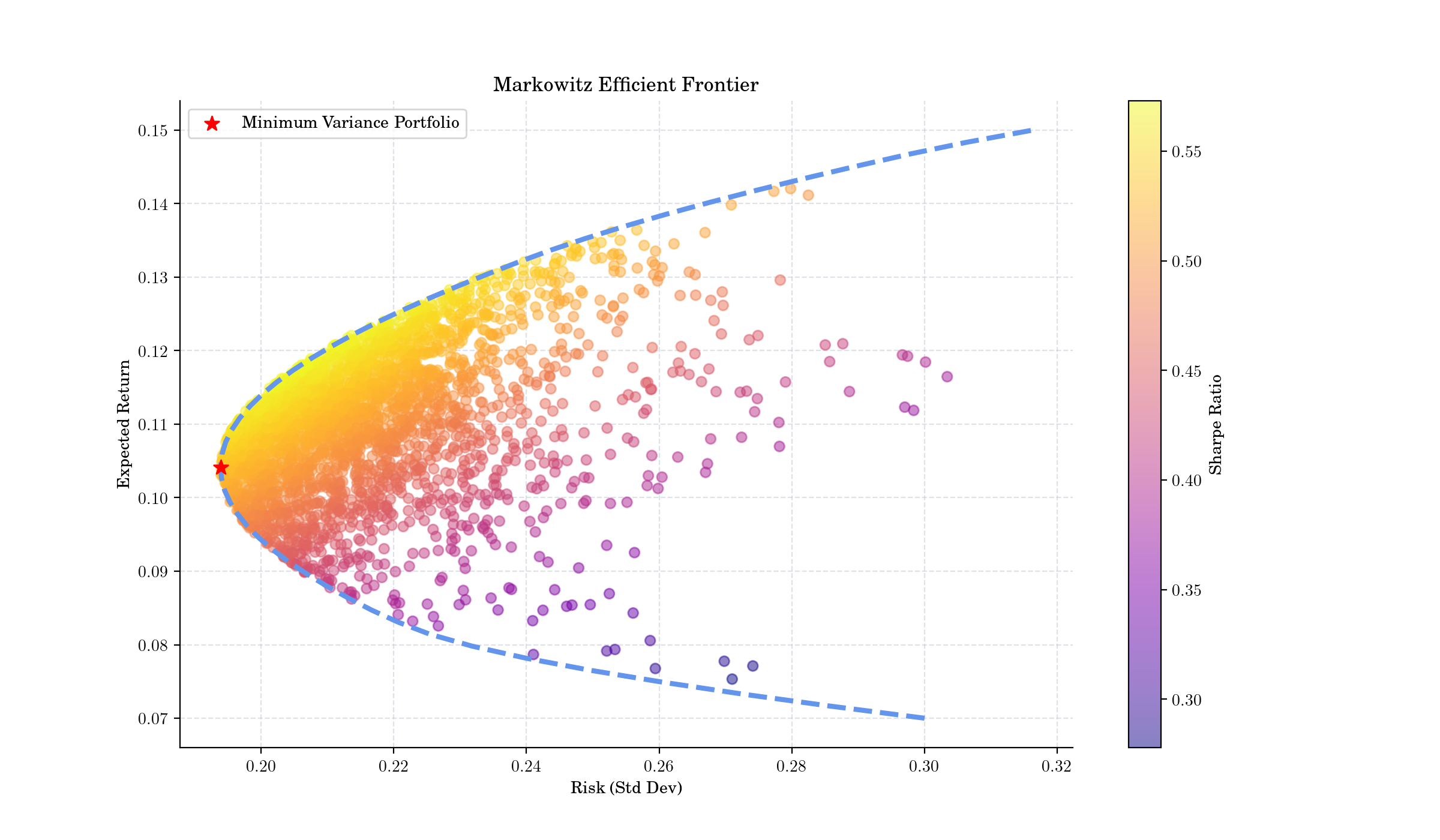
Markowitz Efficient Frontier#
In the plot above, the efficient frontier is depicted as a curve in the risk-return space. The blue dashed line represents the efficient frontier, while the red star indicates the minimum variance portfolio (MVP), which is the portfolio with the lowest risk. The color gradient of the scatter points indicates the Sharpe ratio of the portfolios, which measures the risk-adjusted return. The Markowitz Efficient Frontier provides a framework for investors to make informed decisions about portfolio allocation based on their risk tolerance and return objectives.
Random Facts#
Harry Markowitz was awarded the Nobel Prize in Economic Sciences in 1990 (almost 40 years after the publication of his seminal paper) for his pioneering work in portfolio theory, which laid the foundation for modern financial economics.
The concept of the efficient frontier has been widely adopted in finance and investment management, influencing portfolio construction and asset allocation strategies across the industry.
The efficient frontier assumes that investors are rational and risk-averse, seeking to maximize returns for a given level of risk. However, real-world investor behavior may deviate from these assumptions due to psychological factors and market inefficiencies.
Two-fund separation theorem: With a risk‑free asset, every optimal portfolio is a combination of the risk‑free asset and the tangency (maximum Sharpe) portfolio.
