Day 17: Geometric Brownian Motion#
A Geometric Brownian Motion (GBM) is a continuous-time stochastic process widely used in financial mathematics to model the dynamics of asset prices. It is characterized by the property that the logarithm of the asset price follows a Brownian motion with drift. GBM is particularly popular in option pricing models, such as the Black-Scholes model, due to its ability to capture the random nature of asset price movements while ensuring that prices remain positive.
Definition#
A Geometric Brownian Motion \(S(t), t \geq 0\) is defined by the stochastic differential equation (SDE):
where:
\(\mu\) is the drift coefficient, representing the expected return of the asset.
\(\sigma\) is the volatility coefficient, representing the standard deviation of the asset’s returns.
\(B(t)\) is a standard Brownian motion (Wiener process).
The solution to this SDE can be expressed as:
where \(S(0)\) is the initial asset price at time \(t = 0\).
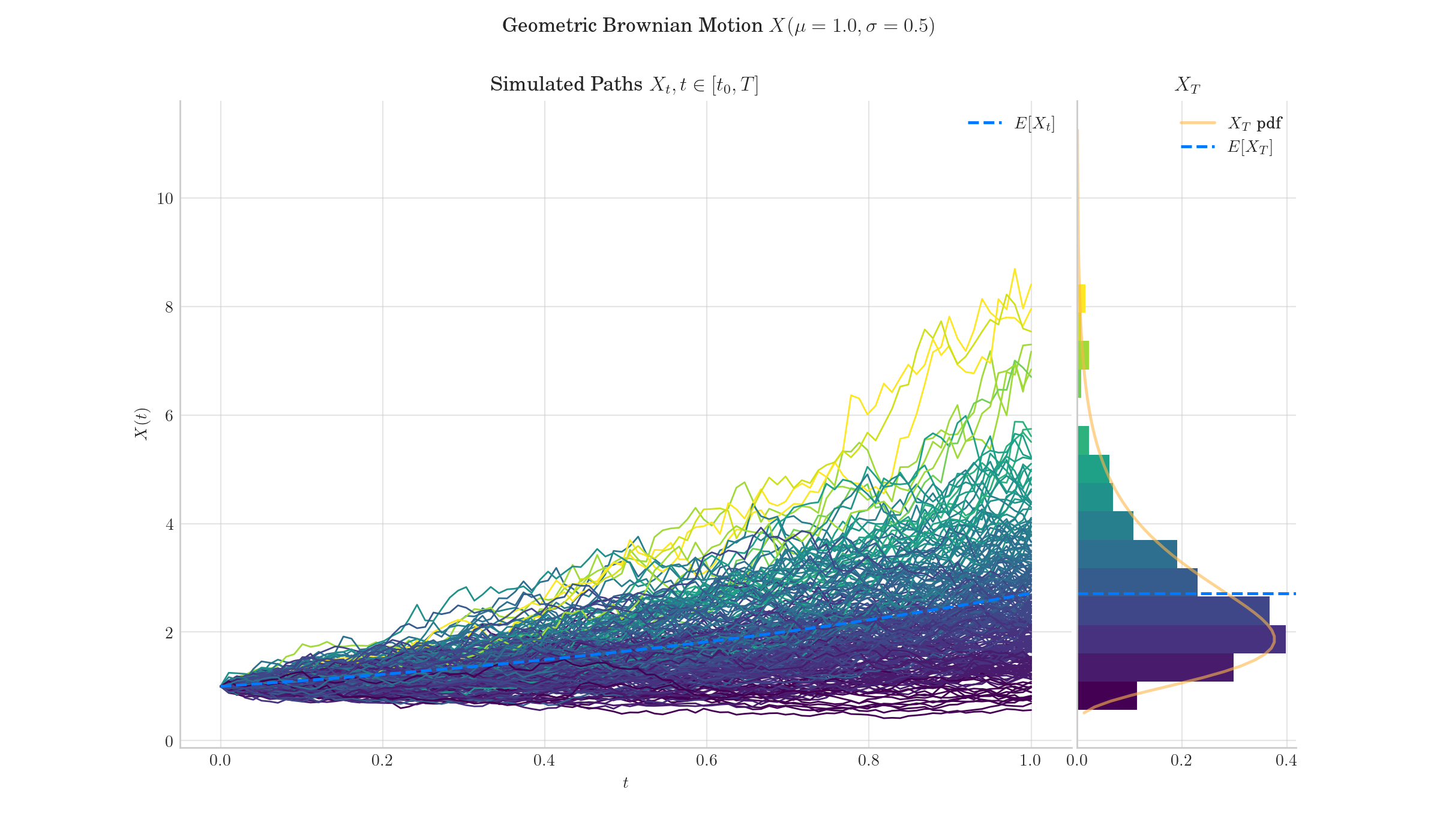
Geometric Brownian Motion Simulation. Image made with aleatory
